(a) Addition reaction
- Occurs when two reactants react to form one product.
- Involves compounds with multiple bonds (unsaturated). The reaction results in breaking of one pi (π) bond to form two sigma (σ) bonds.
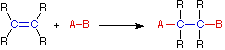
(b) Substitution reaction
- Involves replacing one atom or group with another.
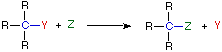
(c) Elimination reaction
- Involves the elimination of two neighbouring atoms from saturated molecules, with the formation of multiple bonds.
- The reverse of addition reaction.
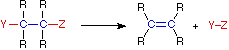
(d) Rearrangement
- Occurs at the transition stage of a reaction involving carbocation.
- Occurs when a single reactant reorganises the bonds or atoms.
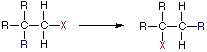
2 comments:
More than 300 different organizations from at least 40 countries worldwide have used Alfa Chemistry's products and services since its inception. Vat Brown 23
Since the syllabus of csir net chemistry coaching is vast, choose the topics that interest you. While doing so also confine mind to not skip the important topics from which questions come consistently in each paper and have more weight you can prepare with best online chemistry classes score good in csir net chemical science coaching
Post a Comment