(a) Most redox reactions are not performed under standard conditions. The cell potential (Ecell) for such a reaction is related to its standard cell potential (Eocell) by Nernst equation.
(b) Consider a redox reaction,
aA + bB → cC + dD
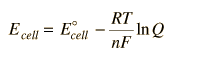

Example:
Zn (s) | Zn2+ (aq, 0.050 M) || Cu2+ (aq, 5.0 M) | Cu (s)
[EoZn2+/Zn = -0.76 V; EoCu2+/Cu = +0.34 V]
Remember the rule in writing cell notation (ABC rule), it shows that zinc half-cell is the anode and copper half-cell is the cathode.
Overall cell reaction equation: Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Since there are 2 mole of electrons transferred, n =2.
Eocell = Eocathode - Eoanode
= +0.34 - (-0.76)
= +1.10 V
(c) For galvanic cell involving gas, the pressure of the gas (in atm) is included in the reaction quotient, Q.
Example:

For the following cell reaction,
Zn (s) + 2 H+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
Determine the concentration of H+ ion if the cell potential at 25oC is +0.45 V, [Zn2+] = 1.0 M and PH2 = 1.0 atm. [EoH+/H2 = +0.00 V; EoZn2+/Zn = -0.76 V]
From the overall cell reaction equation, it shows that zinc half-cell is the anode (since it undergoes oxidation: an increase in oxidation number) and hydrogen half-cell is the cathode (since it undergoes reduction: a decrease in oxidation number).
Eocell = Eocathode - Eoanode
= +0.00 - (-0.76)
= +0.76 V
Since there are 2 mole of electrons transferred, n =2.
(d) At equilibrium, there is no net transfer of electrons. Thus, Ecell = 0 and Q = K, where K is the equilibrium constant.

Eocell = (0.0592/n) log K
Example:
Find the value of the equilibrium constant (K) for the following reaction using standard reduction potential at 25oC.
Cu (s) + 2 Ag+ (aq) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2 Ag (s)
[EoCu2+/Cu = +0.34 V; EoAg+/Ag = +0.80 V]
From the overall cell reaction equation, it shows that copper half-cell is the anode (since it undergoes oxidation: an increase in oxidation number) and silver half-cell is the cathode (since it undergoes reduction: a decrease in oxidation number).
Eocell = Eocathode - Eoanode
= +0.80 - (+0.34)
= +0.46 V
Ecell = Eocell - (0.0592/2) log K
0 = 0.46 - (0.0296) log K
(0.0296) log K = 0.46
log K = 15.54
K = 3.47 x 1015

No comments:
Post a Comment