1. Gas laws
(a) Boyle's law (The pressure – volume relationship)
For a fixed amount of gas at a constant temperature, the volume of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of gas.

(a) Boyle's law (The pressure – volume relationship)
For a fixed amount of gas at a constant temperature, the volume of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of gas.

At constant mass and temperature,

PV = k where k = proportionality constant
At different pressure and volume,
P1V1 = P2V2 where P1 = initial pressure
V1 = initial volume
P2 = final pressure
V2 = final volume
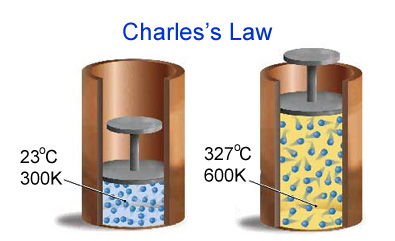
(b) Charles’s law (The temperature – volume relationship)
For a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure, the volume of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (in Kelvin).
At constant mass and pressure,

V/T = k where k = proportionality constant
At different temperature,
 where V1 = initial volume
where V1 = initial volume
T1 = initial temperature
V2 = final volume
T2 = final temperature
(c) Avogadro’s law (The volume – amount relationship)
At constant pressure and temperature, the volume of gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of the gas present.
At constant pressure and temperature,

V/n = k where k = proportionality constant


At standard temperature and pressure (STP),
1 mol of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L
2. Graphs of Gas laws
(a) Boyle's law


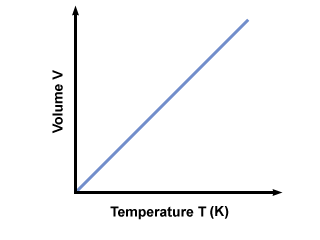
(b) Charles's law

3. Combined gas law (Combination of Boyle's and Charles's law)
At constant mass,
 where P1 = initial pressure
where P1 = initial pressure
V1 = initial volume
T1 = initial temperature
P2 = final pressure
V2 = final volume
T2 = final temperature
4. Ideal gas equation (Combination of Boyle's, Charles's and Avogadro's law)




where R = 0.08206 L atm mol-1 K-1 @ 8.314 J mol-1 K-1
5. Determination of molar mass and density using ideal gas equation


PV = k where k = proportionality constant
At different pressure and volume,
P1V1 = P2V2 where P1 = initial pressure
V1 = initial volume
P2 = final pressure
V2 = final volume
(b) Charles’s law (The temperature – volume relationship)
For a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure, the volume of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (in Kelvin).

At constant mass and pressure,
V/T = k where k = proportionality constant
At different temperature,
T1 = initial temperature
V2 = final volume
T2 = final temperature
(c) Avogadro’s law (The volume – amount relationship)
At constant pressure and temperature, the volume of gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of the gas present.
At constant pressure and temperature,
V/n = k where k = proportionality constant


At standard temperature and pressure (STP),
1 mol of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L
2. Graphs of Gas laws
(a) Boyle's law


(b) Charles's law


3. Combined gas law (Combination of Boyle's and Charles's law)
At constant mass,
 where P1 = initial pressure
where P1 = initial pressureV1 = initial volume
T1 = initial temperature
P2 = final pressure
V2 = final volume
T2 = final temperature
4. Ideal gas equation (Combination of Boyle's, Charles's and Avogadro's law)

where R = 0.08206 L atm mol-1 K-1 @ 8.314 J mol-1 K-1
5. Determination of molar mass and density using ideal gas equation


No comments:
Post a Comment